所属系统:公共技术中心
实验室位置:地4楼(食堂北侧)一层
实验室主任:李金华
实验室简介 | 仪器介绍 | 人员组成 | 工作内容 | 收费标准 | 用户须知 | 欢迎来访
电子显微镜实验室成立于2012年。实验室是研究所构建的微区微量原位分析系统的重要组成部分。目前拥有多台大型分析仪器:扫描电子显微镜(型号Thermoscientific Apreo及型号Nova NanoSEM 450)、聚焦离子束-扫描电子显微镜(FIB/SEM)系统(型号:Zeiss Auriga Compact)、透射电子显微镜(型号:JEM-2100HR TEM)、X射线荧光光谱仪(型号:μ-XRF,型号:Bruker M4 Tornado PLUS)及超景深数码显微镜(型号:Zeiss Smartzoom5)等。实验室对国内外研究人员高质开放。
仪器介绍

一. 透射电子显微镜
透射电子显微镜(型号:JEM-2100HR TEM),能从微纳米尺度对天然矿物、地外陨石、生物合成矿物等样品的形貌、晶体结构(如晶格生长和缺陷)和主量元素等进行高精度分析,获取矿物或岩石的形成、变质/变形及其携带的构造信息。目前服务主要包括形貌观察、点能谱成分分析、高分辨图像及电子衍射分析。基本性能指标:
(1)电子枪:六硼化镧(LaB6)灯丝;加速电压: 200kV。
(2)分辨率:点分辨率:0.23nm,线分辨率:0.14nm。
(3)附件:X-MAX TEM电制冷能谱仪用于点成分分析。
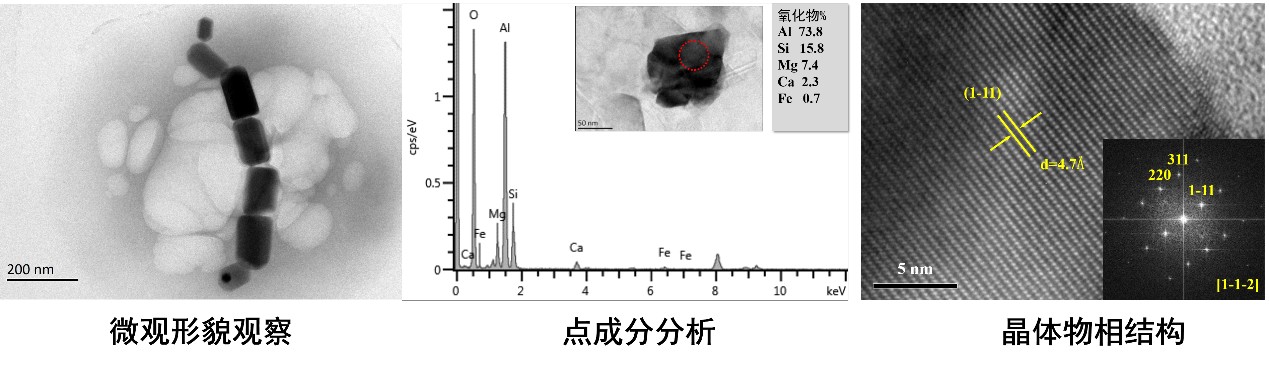
基本性能指标:
1. 电子枪:六硼化镧(LaB6)灯丝;加速电压: 80,100,120,160,200kV;
2. 分辨率:点分辨率:0.23nm,线分辨率:0.14nm;
3. 附件:X-MAX TEM电制冷能谱仪用于点成分分析。
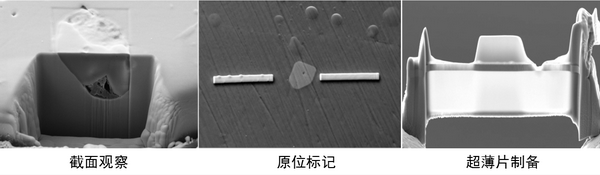
二. 聚焦离子束-扫描电子显微镜双束系统
聚焦离子束-扫描电子显微镜(FIB/SEM)系统(型号:Zeiss Auriga Compact),主要用于表面二次电子形貌观察、能谱面扫描、样品截面观察、微小样品标记以及TEM超薄片样品的制备。基本性能指标:
(1)SEM: 加速电压0.1 - 30 kV,肖特基场发射灯丝,2.5 nm @ 1 kV 在最佳WD。
(2)FIB:加速电压0.5 - 30 kV,带有镓液态金属离子源,分辨率5 nm (30 kV, 1 pA)。
(3)附件:OmniProbe 200纳米操作机械手及X-MAX80电制冷能谱仪(EDS) 。
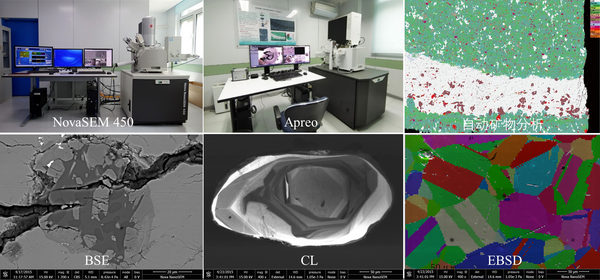
扫描电子显微镜(型号:Nova NanoSEM 450和Thermoscientific Apreo),能够获得优异的背散射和形貌图像,并可以获得整个薄片的背散射图像和能谱元素mapping。另外,Nova NanoSEM 450还可以拍摄阴极发光图像(CL)、电子背散射衍射(EBSD);Thermoscientific Apreo可以进行陨石、页岩和稀土等样品的自动矿物分析,寻找特定矿物并获得主要矿物的矿物含量及分布。基本性能指标:
(1)电子束分辨率在高真空条件下优于1.0 nm
(2)Nova NanoSEM 450上配备牛津仪器X射线能谱仪(型号X-MAXN80)、电子背散射衍射仪 (型号Nordlys Nano探测器)以及Gatan公司CL阴极发光光谱仪(型号MonoCL4)。
(3)Thermoscientific Apreo上配备X射线能谱仪(型号:Bruker XFlash 60)、大面积拼图及自动矿物分析软件(Maps-Nanomin)。
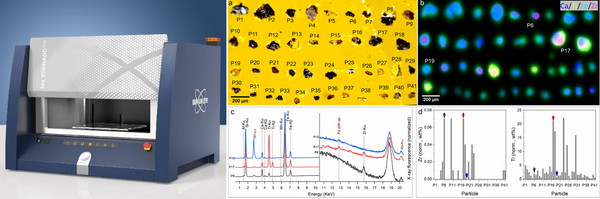
四. 高分辨率显微X射线荧光光谱仪
高分辨率显微X射线荧光光谱仪μ-XRF(型号:μ-XRF,型号:Bruker M4 Tornado PLUS)主要用于对样品进行无损元素分析,获得高分辨率元素分布扫描图,输出能谱和定量结果。基本性能指标:
(1)多毛细管X射线光学,<20 μm的光斑大小(Mo-K),能满足元素C6-U92的成分分析。
(2)高分辨的μ-XRF,景深可高达±5 mm,不平的样品也可以获得极佳分辨率。
五. 超景深数码显微镜及偏光显微镜
超景深数码显微镜(型号:Zeiss Smartzoom5),可对样品进行三维成像,大范围高速图像拼接,拥有数码变倍及光学变焦、实现数码显微镜无极连续变倍,可快速便携地对样品进行二维、三维的观察和测量。基本配置:(1)载物台:尺寸310mm×220mm,载荷4kg,行程(XY):130mm×100mm;行程(Z):60 mm;(2)光学变倍系数10x,最大倍数2021倍;(3)物镜:平场复消色差物镜 1.6x、5.0x、10x。
偏光显微镜(型号:Nikon LV100N POL),能够实现岩石光薄片的透反射偏光、荧光观察。基本配置:(1)目镜:10x (F.O.V. 22mm),匹配透反射光、荧光功能;(2)匹配5X\10X\50X\100X物镜。

实验室成员
 |
实验室主任:李金华研究员 |
 |
技术人员:谷立新高级工程师 |
 |
技术人员:唐旭工程师 |
|
学生助管:朱珂磊,办公室:地1楼1015(负责XRF)电话:18800295103 | |
工作内容:
本实验室主要进行的分析测试工作参考设备介绍,以下为实验条件说明及主要论著及方法:
电子显微镜实验室:Electron Microscopy Laboratory, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS)
备注:仪器测试分析条件仅供参考,方法引用可参考列表文章,注意避免雷同。
1. 聚焦离子束显微镜(FIB-SEM)
节选自(Lixin Gu , GRL, 2022)供参考:Two ultra-thin foils (~100 nm in thickness) were prepared using the Zeiss Auriga Compact FIB-SEM at IGGCAS. Ion beam conditions for milling and final polishing were 5–30 kV high voltage with various beam currents (20 pA–4 nA).
2. 透射电子显微镜(TEM)
The TEM bright-field(BF)/dark-field(DF) imaging, selected area electron diffraction (SAED) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) imaging were carried out using a JEOL JEM-2100 TEM operated at 200 kV, electron beam generated from a LaB6 gun at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese academy of sciences (IGGCAS).
3. 扫描电镜(SEM)
普通SEM拍照可以看图像底部的使用条件。
如果做矿物分析可引用(Lixin Gu , American Mineralogist, 2022)供参考:Mineral assemblages and mineral distribution features of samples were conducted using the Thermofisher Apreo field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) equipped with a Bruker XFlash 60 energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) detector utilizing the MAPS-Naomin automated mineralogy software at IGGCAS (Gu et al., 2022). The instrument was operated at a accelerating voltage of 25 kV with beam current of 13 nA. X-ray for mineral analyses was collected with a step size of 15 μm and a dwell time of 8 ms.
4. X射线显微镜(SEM)
节选自(Jin-HuaLi, Geoscience Frontiers, 2022)供参考:All the scanning μXRF element mapping experiments were performed with an X-ray tube energy of 50 kV and a current of 600 μA, with 40 ms per pixel spectrum acquisition time and a pixel step-size of 9 μm. Data analyses including obtaining elemental maps on all objects and XRF spectrum from each object or region of interest were undertaken with the characterization software provided by Bruker Micro Analytics.(更多详情请参考列表相关文章)
5. 关于致谢(Acknowledge)
(1) 凡出自本实验室的实验数据发表的文章,请务必按照规范在方法或致谢中提及相应的设备和技术人员的支撑工作(仅便于仪器的成果统计)。
举例:We thank XXX at the Electron Microscopy Laboratory, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (EML, IGGCAS), for their efforts to maintain operation in FIB-SEM /(&) TEM experiments.
6. 关于挂名(Co-Author)
对文章挂名不做要求。测试者可根据技术人员的贡献,自行选择。由本室实验数据产出的成果越多,实验会予以优先安排。
7. 部分文章列表
实验室成果:
(1)Li J H, Li Q L, Zhao L, et al. Rapid screening of Zr-containing particles from Chang’e-5 lunar soil samples for isotope geochronology: Technical roadmap for future study. Geoscience Frontiers, 2022, 13(3): 101367.(月壤单颗粒研究)
(2)Li J, Liu P, Menguy N, et al. Identification of sulfate‐reducing magnetotactic bacteria via a group‐specific 16S rDNA primer and correlative fluorescence and electron microscopy: Strategy for culture‐independent study[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2022.(趋磁细菌研究策略)
(3)Lixin Gu, Yongjin Chen, Yuchen Xu, Xu Tang, Yangting Lin, Takaaki Noguchi, Jinhua Li, 2022, Space Weathering of the Chang'e‐5 Lunar Sample From a Mid‐High Latitude Region on the Moon. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(7): e2022GL097875.(FIB-TEM)
(4)Lixin Gu, Sen Hu, Mahesh Anand, Xu Tang, Jianglong Ji, Bin Zhang, Nian Wang, Yangting Lin, 2022, Occurrence of tuite and ahrensite in Zagami and their significance for shock-histories recorded in Martian meteorites. American mineralogist, 107(6): 1018-1029.(FIB-TEM及自动矿物分析)
(5)Xu Tang, Qiu-Li Li, Bin Zhang, Peng Wang, Li-Xin Gu, Xiao-Xiao Ling, Chen-Hui Fei, Jin-Hua Li. 2020.The Chemical State and Occupancy of Radiogenic Pb, and Crystallinity of RW-1 Monazite Revealed by XPS and TEM. Minerals.10:504. (FIB-TEM)
(6)Lixin Gu, Bin Zhang, Sen Hu, Takaaki Noguchi, Hiroshi Hidaka, Yangting Lin, The Discovery of Silicon Oxide Nanoparticles in Space-weathered of Apollo 15 Lunar Soil Grains, Icarus, 303 (2018) 47–52.(FIB-TEM)
(7)Xu Tang, Li Xin Gu, Qiu Li Li, Zhong Ming Du, Sai Hong Yang, Lian Jun Feng, Jin Hua Li. An apparatus for plasma cleaning and storage of transmission electron microscopy specimens and specimen holders. Microscopy Research and Technique, 2022: 1-10.(TEM)
(8)Yan Liu, Chaoqun Zhang, Di Zhang,d Tong Liu,d Hao Qiu, Qiu-Li Li, and Jin-Hua Li, Non-destructive Micro X-ray Fluorescence Quantitative Analysis of Geological Materials, Atomic Spectroscopy, 2022, 43 (05).(XRF)
(9)Chaoqun Zhang and Jin-Hua Li, Non-destructive Identification and quantification of Ilmenite from a Single Particle of the Chang’E-5 Lunar Soil Sample, Atomic Spectroscopy, 2022, 43 (4), 284-291.(XRF)
(10)Jinhua Li, Rui Pei, Fangfang Teng, Hao Qiu, Roald Tagle, Qiqi Yan, Qiang Wang, Xuelei Chu, and Xing Xu, Micro-XRF Study of the Troodontid Dinosaur Jianianhualong Tengi Reveals New Biological and Taphonomical Signals, Atomic Spectroscopy, 2021, 42 (1), 1-11.(XRF)
(11)唐旭,李金华. 透射电子显微镜技术新进展及其在地球和行星科学研究中的应用. 地球科学. 2021. 46(4): 1374-1415.(TEM)
(12)李金华, 潘永信. 透射电子显微镜在地球科学研究中的应用. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(9): 1359-1382.(TEM)
(13)谷立新, 李金华. 聚焦离子束显微镜技术及其在地球和行星科学研究中的应用. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(6): 1119-1140.(FIB-SEM)
部分合作成果:
(1) Li Q L, Zhou Q, Liu Y, et al. Two-billion-year-old volcanism on the Moon from Chang’e-5 basalts. Nature. 2021. 600: 54-58.(行星科学)
(2)Hu S, He H, Ji J, et al. A dry lunar mantle reservoir for young mare basalts of Chang’e-5. Nature. 600: 49-53.(行星科学)
(3)Liu C, Tang X, Cheng L, et al. The characterization of corrosion layers of GH3535 and Inconel 625 alloys in molten KNO3-NaNO3 salts at 500 °C. Corrosion Science. 2022. 204: 110406.(材料科学)
(4)Cai Y, Wang Y, Xu H, et al. Positive magnetic resonance angiography using ultrafine ferritin-based iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale, 2019. 11(6): 2644-2654. (生物地磁)
(6)Yang J, Zhang C, Miyahara M, et al. Evidence for early impact on a hot differentiated planetesimal from Al-rich micro-inclusions in ungrouped achondrite Northwest Africa 7325. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 2019. 258: 310-335.(行星科学)
(7)Jiang X D, Zhao X, Chou Y M, et al. Characterization and quantification of magnetofossils within abyssal manganese nodules from the western Pacific Ocean and implications for nodule formation. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 2020. 21: e2019GC008811.(生物地磁)
(8)Guo S, Hermann J, Tang P, et al. Formation of carbon-bearing silicate melts by melt-metacarbonate interaction at convergent plate margins. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2022, 597: 117816. (地质学)
(9)Liu X, Su B X, Bai Y, et al. Genesis of “silicate exsolution lamellae” in chromite of the Stillwater Complex: A challenge to the high-pressure crystallization of ophiolitic chromitite. Lithos. (2020)378–379: 105796.(地质学)
收费标准
|
类别 |
所外 |
所内 |
备注 |
| FIB | 1500元/小时 | 1200元/小时 | 制备TEM薄片按样收费 |
| SEM | 600元/小时 | 500元/小时 | 非常规测试单独计费 |
| TEM | 600元/小时 | 600元/小时 | 非常规测试单独计费 |
| XRF | 400元/小时 | 300元/小时 | |
| Smartzoom | 200元/小时 | 100元/小时 | |
| 偏光显微镜 | 200元/小时 | 100元/小时 |
用户须知
(1)提前致电010-82998592进行实验预约和咨询样品是否适宜上机分析。
(2)组内通过考核者可以直接扫描二维码进行预约(新用户在注册时一定要准确填写姓名和电话)。

欢迎来访
实验室位于北京市朝阳区北土城西路19号,健德桥东100米,邮编100029。中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所,地4楼(食堂北侧)一层。电话:010-82998592。
