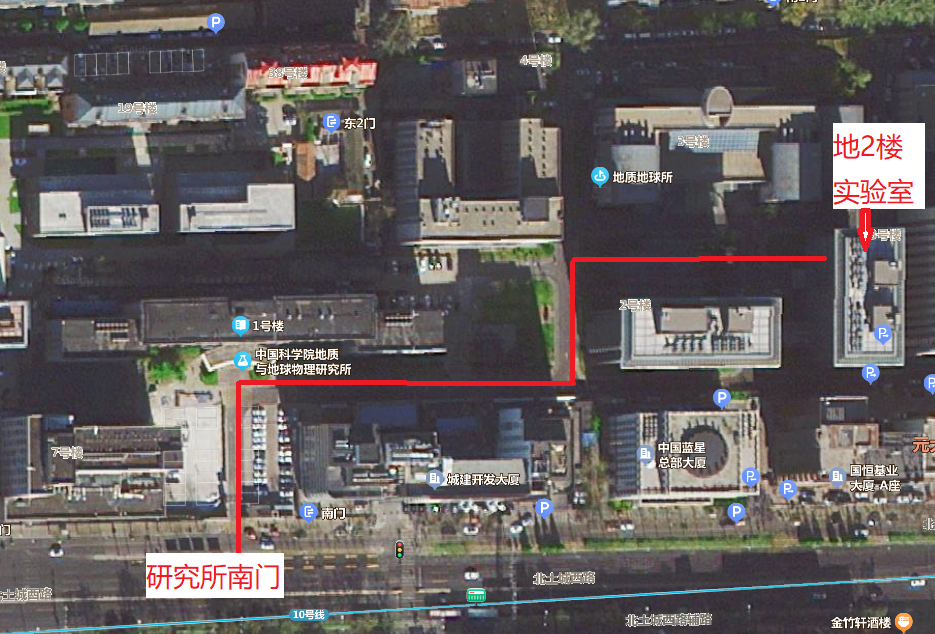
所属系统:地质年代学测定系统
实验室位置:地2楼205
实验室主任:杨列坤 副研究员
实验室概况 | 仪器介绍 | 实验室成员 | 工作内容 | 收费标准 | 欢迎来访
40Ar/39Ar和(U-Th)/He年代学实验室拥有多台先进的稀有气体质谱仪和激光探针系统,是国内重要的年代学和热年代学研究平台。40Ar/39Ar法是年代学中的重要手段,测年范围从46亿年的陨石到数千年的火山岩,研究领域从行星演化到地球动力学,从古环境与气候到考古研究,从岩浆活动到板块运动,从元素运移到成矿机制等,涉及到地球与行星科学的各个方面;测年物质广泛,几乎涵盖了所有的的含钾矿物;测年精度高,是确定地质年表及地磁极性年表时标的主要手段。 (U-Th)/He是近二十年来快速发展起来的低温(热)年代学方法,其成功应用大大延伸了中低温热年代学(如40Ar/39Ar,裂变径迹)的温度下限,使其在新构造地质、地貌演化、环境变迁等重大地质问题的研究中具有广阔的应用前景。
长期以来,我们始终把提高定年精度作为主线,加强优势领域的研究,发挥40Ar/39Ar法的独特优势,拓展新的应用方向,建立新的国际标准样品,建设高水平的实验室平台。目前实验室超低的本底水平使得我们能进行微量样品的定年及(超)年轻样品的40Ar/39Ar定年,成为实验室的重要特色之一;同时秉承理论-实验-模拟的理念,发挥40Ar/39Ar热年代学定量的优势,为地质过程热历史的恢复提供最佳模拟手段,进而为深部动力学机制研究提供定量制约。近期结合特提斯演化这一综合科学问题,实验室培育了造山带演化、成矿机制、新生代地貌地形演化历史研究等重要发展方向。
实验室自建立伊始,一直坚持开放共享的理念,成为全球开放的年代学和热年代学知名研究平台,为国内外的地质学家提供了广泛的实验研究;鼓励学生和研究人员到实验室开展研究工作,实地参与样品分析、数据处理和结果解释;广泛参与国际交流,2013年成功举办了Ar-Ar和(U-Th)/He国际研讨会,主持了由澳大利亚Curtin大学、法国国家科研中心、台湾大学、法国蒙彼利埃大学等Ar-Ar实验室参与的国际实验室对比标定计划。
实验设备:
1) Noblesse 稀有气体质谱仪 (英国Nu Instruments公司),2014年安装,Noblesse采用高效率NIER离子源,新颖的多接收器设计,自动变焦离子镜,先进的仪器控制系统,数据采集和处理系统,显著提高了同位素比值的分析精度,主要应用于激光微量及微区原位Ar-Ar定年和(超)年轻样品的定年。

2)MM5400 稀有气体质谱仪(英国GV 公司),2003年安装,具有低本底、高灵敏度和适中的分辨率,主要用于常规阶段升温Ar-Ar定年和热年代学实验模拟研究。

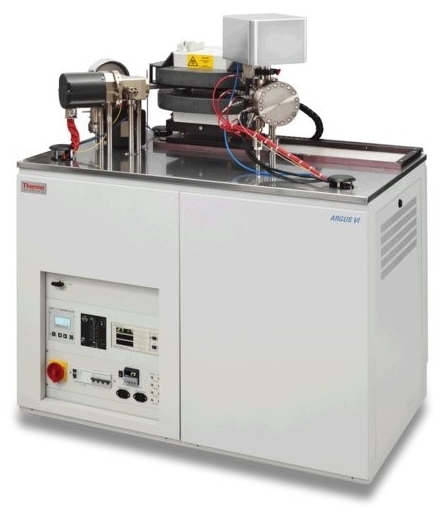
3)Argus VI 稀有气体质谱仪(Thermo Fisher Scientific公司),2022年安装。ArgusVI是针对氩同位素分析设计的小体积多接收质谱仪。仪器根据氩同位素丰度配备了不同的法拉第杯高阻以及电子倍增器,结合独特的离子束偏转技术可以实现动态多接收以及36Ar等小信号同位素的高精度测量。

4)Photon Machine公司 Analyte G2激光剥蚀系统,配备紫外193nm准分子激光器,2014年安装,用于激光微区原位Ar-Ar定年。

5)美国New Wave 公司MIR10红外激光熔样系统,2004年安装,主要用于单颗粒及多颗粒矿物激光全熔或阶段升温Ar-Ar定年。

6)美国Teledyne Photon Machines公司的10.6 Fusion CO2激光熔样系统,2020年安装,主要用于阶段升温或单颗粒全熔Ar-Ar定年。
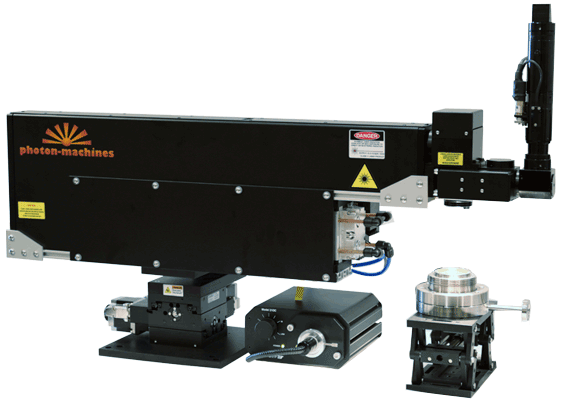

7)美国Teledyne Photon Machines公司的二极管激光熔样系统,2020年安装,主要用于群体矿物的阶段升温Ar-Ar定年。激光配备了红外测温系统,可实时监测加热过程的温度变化。

8)澳大利亚科学仪器公司 AlphachronTM He同位素提取系统及四级杆质谱仪,借助精确标定的3He稀释剂,能够准确测定4He的绝对含量,本底低至0.0015 ncc STP

9) Thermo Fisher X2 系列 电感耦合等离子质谱用于U、Th同位素测试,可同时进行U-Pb定年和微量元素分析

10)Resonetics M-50 准分子激光剥蚀系统,最大能量200 mJ(锆石的原位分析通常用90 mJ)用于锆石原位微区分析,是激光原位锆石(U-Th)/He和U-Pb双定年的重要工具

11) 澳大利亚Autoscan公司最新Trackscan裂变径迹测试系统,硬件基于蔡司M2m自动显微镜和高精度电控载物台,软件为墨尔本大学开发的控制软件TrackWorks和离线处理软件FastTracks

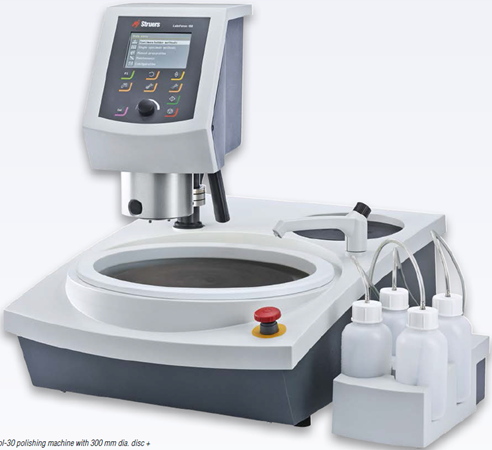
12)司特尔LaboSystem自动研磨抛光机,可精确控制磨盘和机头转速以及单点压力。用于裂变径迹、原位Ar-Ar和 (U-Th)/He的样品前处理
|
|
杨列坤 实验室主任 博士,副研究员,负责实验室研究发展方向及实验室管理 办公室:地3楼311室 |
|
|
吴林 博士,高级工程师,负责U-Th/He年代学分析测试,接收样品,数据处理及发放 办公室:地1楼208 |
|
|
师文贝 博士,高级工程师 ,负责常规及微区Ar-Ar年代学分析测试,仪器运行维护,数据处理及发放 办公室:地1楼208 |
|
|
王银之 博士,工程师 ,负责样品接收及辐照,年轻样品分析测试,仪器运行维护,数据处理及发放 办公室:地1楼208 |
本实验室主要进行如下方面的分析测试工作:
实验室建立了完整的Ar-Ar和(U-Th)/He年代学技术体系。其中Ar-Ar定年包括常规阶段升温技术,激光阶段升温技术,单颗粒矿物的激光全熔或阶段升温测定,激光微区原位(通常10-50微米)定年,定年矿物涵盖碱性长石、斜长石、云母,角闪石等常见造岩矿物及火山岩基质,为满足不同地质研究的需求有针对性的设计了相应的实验流程。(U-Th)/He定年方法目前主要包括磷灰石和锆石的单颗粒溶液法定年,锆石的激光原位(U-Th)/He和U-Pb双定年。
主要应用领域:
(1)火山岩及火山沉积地层定年:快速冷却的火山岩是40Ar/39Ar法定年的良好对象,为地层划分和地磁极性确定以及火山活动提供有效的研究手段
(2)构造-热年代学:利用不同矿物的封闭温度及封闭时间和同一矿物中多重扩散域特征,建立中上地壳侵入岩及变质岩的冷却历史,进而探索岩体的抬升过程。发挥Ar-Ar和(U-Th)/He的优势,恢复地质体的抬升和冷却历史、地形的演化过程
(3)微区年代学:结合聚焦<10μm的紫外激光探针测定单颗粒矿物中气体同位素浓度分布,进而探索年龄分布,为反推地质体热历史和变质变形过程提供有力的微区研究手段
(4)稀有气体(如He、Ar)扩散机制的研究,探索气体扩散和温度的关系、矿物封闭机制,架起实验和地质过程的桥梁
送样要求及联系人:
Ar-Ar定年送样要求:
新鲜含钾矿物(如碱性长石、斜长石、云母、角闪石、火山岩基质等),粒度40-60目或60-80目,样品纯净,重量100mg以上,特殊矿物定年、原位微区定年和超年轻地质体定年请联系实验室工作人员。
联系人:师文贝,shiwenbei@mail.iggcas.ac.cn, 010-82998560
(U-Th)/He定年送样要求:
样品分析采用单颗粒熔融法,每个样品分析3-5个颗粒, 测试矿物主要为磷灰石和锆石。要求矿物晶体新鲜、自形好,磷灰石和锆石宽度通常不少于70微米,长度大于100微米。每个样品要求20-50个自形晶体颗粒。如需进行锆石(U-Th)/He和U-Pb双定年,用户需自行制靶(Teflon靶,环氧树脂锆石靶在提取4He时会影响系统的真空度以及本底)并拍摄阴极发光图像,并且自行选取激光剥蚀位置。为获得颗粒完整的磷灰石或锆石,鼓励用户亲自碎样、选矿。
联系人:吴林,wulin08@mail.iggcas.ac.cn,010-82998560
实验方法及应用相关论文:
1. Xiang DF et al., 2025, Late Miocene rapid exhumation in the West Kunlun range: Insights into Tibetan Plateau growth and India-Asia lithospheric collision, Geology, DOI: 10.1130/G53642.1.
2. Guo C et al., 2025, Apatite Geo‐Thermochronology and Geochemistry Constrain Oligocene‐Miocene Growth and Geodynamics of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, Geophysical Research Letters, 52(4), DOI: 10.1029/2024GL113157.
3. Wang YZ et al., 2025, Challenges in Interpreting 40Ar/39Ar Age Spectra: Clues from Hydrothermally Altered Alkali Feldspars Geosciences 15, no. 5: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15050188.
4. 安洁等,2024,综合定年标准样品研制-以青藏高原伦坡拉盆地丁青湖组凝灰岩为例,岩石学报,40(8),2306-2320,doi:10.18654/1000-0569/2024.08.00. (Corresponding author)
5. An J et al., 2024, Vesuvianite: A new mineral species of (U-Th)/He geochronology, Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, DOI: 10.1039/d4ja00127c. (Corresponding author)
6. Wang YZ et al., 2024, Qingshan sanidine (QSs): A new mesozoic 40Ar/39Ar dating standard tied to the M0r (Barremian–Aptian boundary), Applied Geochemistry, DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2024.105932.
7. Yang F et al., 2024, Prolonged exhumation and preservation of the Yuku molybdenum ore field, East Qinling, China: Constraints from medium- to low-temperature thermochronology, Ore Geology Reviews, 105973, DOI: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.105973.\
8. Xiang DF et al., 2024, Cenozoic pulsed rise and growth of the Chinese South Tianshan revealed by zircon and apatite provenance analyses: Implications for stepwise aridification in the Tarim Basin, Tectonics, DOI: 10.1029/2023TC008211.
9. Xiang DF et al., 2024, Exhumation and preservation of the Baixintan magmatic Ni-Cu sulphide deposit: Insights from (U-Th)/He and fission track thermochronology, Ore Geology Reviews, DOI: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.106411.
10. Zhang ZY et al., 2023, From Tethyan subduction to Arabian-Eurasian continental collision: multiple geochronological and thermochronological signals from granitoids in the Azerbaijan region (NW Iran), Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 111567. DOI: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111567.
11. Wang YZ et al., 2023, Alder Creek sanidine (ACs-a): A new sampling and intercalibration of Quaternary 40Ar/39Ar age monitor, Applied Geochemistry, 152, 105629, DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.
12. Wang N et al., 2023, Late Mesozoic impact of Paleo-Pacific subduction on the North China craton revealed by apatite U-Pb and fission-track double dating and REE analysis in the eastern Yanshan fold belt, northeastern China, Geological Society of America Bulletin, DOI: 10.1130/B36751.1.
13. Wu L et al., 2023, SA01: A new potential reference material for zircon in-situ (U-Th)/He and U-Pb double dating, Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, doi:10.1039/d2ja00348a.
14. Zhang WB et al., 2022, Mountain growth under the combined effects of paleostress and paleoclimate: Implications from apatite (U-Th)/He thermochronology on Taibai Mountain, central China, Lithosphere, 8286127, 10.2113/2022/8286127.
15. Zhang WB et al., 2022, Reactivated margin of the western North China Craton in the Late Cretaceous: Constraints from zircon (U-Th)/He thermochronology of Taibai Mountain,Tectonics, DOI: 10.1029/2021TC007058.
16. Guo C et al., 2022, Late Cenozoic topographic growth of the South Tianshan Mountain Range: Insights from detrital apatite fission-track ages, northern Tarim Basin margin, NW China, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 234, 105227.
17. Wang YZ et al., 2022, An investigation of factors affecting the reproducibility of (U–Th)/He ages of high- and low-U minerals, Geochemical Journal, 56(4), 96-111.
18. Wu L et al., 2021, Reappraisal of the applicability of MK-1 apatite as a reference standard for (U-Th)/He geochronology, Chemical Geology, 575, 120255.
19. Xiang DF et al., 2021, Apatite U–Pb dating with common Pb correction using LA–ICP–MS/MS, Geostandard and Geoanalytical Research, 45(4), 621-642.
20. Wang N et al., 2021, Pulsed Mesozoic exhumation in Northeast Asia: New constraints from zircon U-Pb and apatite U-Pb, fission track and (U-Th)/He analyses in the Zhangguangcai Range, NE China, Tectonophysics, DOI: 10.1016/j.tecto.2021.229075.
21. Gong L et al., 2021, Exhumation and Preservation of Paleozoic Porphyry Cu Deposits: Insights from the Yandong Deposit, Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Economic Geology, 116(3), 607-628.
22. Wu L et al., 2020, Meso-Cenozoic uplift of the Taihang Mountains, North China: Evidence from zircon and apatite thermochronology. Geological Magazine, 157(7), 1097-1111.
23. Wang YZ et al., 2020, Timing and Processes of Ore Formation in the Qingchengzi Polymetallic Orefield, Northeast China: Evidence from 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology, Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(3), 789-800.
24. Shi WB et al., 2020, 40Ar/39Ar dating of basic–felsic dikes in the Sulu Orogen, Shandong Peninsula, China: Evidence for the destruction of the southeastern North China Craton, Geological Journal, 55(7), 5574-5593.
25. Wu L et al., 2019, MK-1 apatite: A new potential reference material for (U-Th)/He dating, Geostandard and Geoanalytical Research, 43(2), 301-315.
26. Wu L et al., 2018, Multi-phase cooling of Early Cretaceous granites on the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Evidence from 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 160, 334-347.
27. Shi WB et al., 2018, Diachronous growth of the Altyn Tagh Mountains: Constraints on propagation of the Northern Tibetan margin from (U-Th)/He dating. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(7), 6000-6018.
28. Shi WB et al., 2018, A prolonged Cenozoic erosional period in East Kunlun (Western China): Constraints of detrital apatite (U-Th)/He ages on the onset of mountain building along the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 151, 54-61.
29. Wang YZ et al., 2018, (U-Th)/He thermochronology of metallic ore deposits in the Liaodong Peninsula: Implications for orefield evolution in the northeast China, Ore Geology Reviews, 92, 348-365.
30. Wu L et al., 2017, Cretaceous exhumation of Proterozoic carbonatite on the northern margin of the North China Craton constrained by apatite fission track and (U-Th)/He geochronology, The Journal of Geology, 125(5), 593-606.
31. Wang F et al., 2017, Differential growth of the northern Tibetan margin: evidence for oblique stepwise rise of the Tibetan Plateau, Scientific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/srep41164
32. Wu L et al., 2016, Cenozoic exhumation history of Sulu terrane: Implications from (U–Th)/He thermochrology. Tectonophysics, 672–673, 1-15.
33. Wang F et al., 2016, Relief history and denudation evolution of the northern Tibet margin: constraints from 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He dating and implications for far-field effect of rising plateau, Tectonophysics, 675, 196-208.
34. Wu L et al., 2014, Rapid cooling of the Yanshan Belt, northern China: constraints form 40Ar/39Ar thermochronology and implications for cratonic lithospheric thinning. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 90, 107-126.
35. Yang L.K. et al., 2014. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of Holocene volcanic activity at Changbaishan Tianchi volcano, Northeast China. Quaternary Geochronology, 21, 106-114.
36. Wang F et al., 2014, YBC sanidine: A new standard for 40Ar/39Ar dating. Chemical Geology, 388, 87-97.
37. Wang F et al., 2013, 40Ar/39Ar Thermochronology on Central China Orogen: Cooling, Uplift and Implications for the Orogeny Dynamics. In: F. Jourdan, D.F. Mark, C. Verati Eds., 40Ar/39Ar dating: from geochronology to thermochronology, from archaeology to planetary sciences. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 378, http://dx.doi.org/10.1144/SP378.3
本实验室数据支持发表的应用论文:
1. 皮静怡等,2025,喜马拉雅琼嘉岗矿区低温热年代学对矿床抬升剥露的制约,岩石学报,41(3),771-788.
2. Zhao YL et al., 2024, Episodic magmatism of the Gongga batholith (eastern Tibet) revealed by detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology: with insights into the Xianshuihe fault activity, Geosphere, https://doi.org/10.1130/GES02692.1.
3. Lu HJ et al., 2024, Lithospheric strike-slip faulting in central Tibet since 35-32 Ma, National Science Review, DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwae428.
4. Li J et al., 2023, Tectonic setting of metamorphism and exhumation of eclogite-facies rocks in the South Beishan orogeny, northwestern China, Geosphere, 19(1), 100-138.
5. 李晨星等,2022,华北克拉通北缘中-新元古界构造-热演化:来自锆石(U-Th)/He年龄的约束,地质力学学报,28(1), 113-125.
6. 林旭等,2022, 苏鲁造山带东段新生代构造隆升及其地质意义:来自磷灰石(U-Th)/He热年代学的约束, 地球科学,47(4), 1162-1176.
7. Yang HH et al., 2022, Thermal history of the Naruo porphyry deposit in the Duoling ore district, Western Tibet: Evidence from U-Pb, 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology, Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 96(6), 2015-2027.
8. Yang HH et al., 2022, The preservation mechanism of the Duolong ore district in northwest Tibet: Evidence from the low temperature thermochronological study, Ore Geology Reviews, 143, 104766.
9. Pang Y M et al., 2022, Emplacement and exhumation history of Mesozoic granitic rocks in the Jiaonan uplift, eastern China, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 234, 105289.
10. Shen P et al., 2022, Newly-recognized Triassic highly fractionated leucogranite in the Koktokay deposit (Altai, China): Rare-metal fertility and connection with the No. 3 pegmatite, Gondwana Research, 112, 24-51.
11. Xin GY et al., 2022, Subduction initiation in the Neo-Tethys and formation of the Bursa ophiolite in NW Turkey, Lithos, 422-423, 106746.
12. 贠晓瑞等,2021,青海共和盆地东北缘中-新生代热演化历史:来自沟后杂岩体及当家寺岩体的低温热年代学证据,岩石学报,37(10), 3241-3260.
13. Zhao WC et al., 2021, Thermochronological constraints on the exhumation history of the Carboniferous Katebasu gold deposit, western Tianshan gold belt, NW China, Geological Society London Special Publications, 516, https://doi.org/10.1144/SP516-2020-201.
14. Wang YS et al., 2021, Exhumation history of late Mesozoic intrusions in the Tongling–Xuancheng area of the Lower Yangtze region, eastern China: Evidence from zircon (U–Th)/He and apatite fission track thermochronology, Ore Geology Reviews, 135, 104220.
15. Du JX et al., 2021, Cenozoic tectono-geomorphic evolution of Yabrai Mountain and the Badain Jaran Desert (NE Tibetan Plateau margin), Geomorphology, 389, 107857.
16. Chu Y et al., 2021, Tectonic exhumation across the Talesh-Alborz Belt, Iran, and its implication to the Arabia-Eurasia convergence, Earth Science Reviewes, 221, 103776.
17. Lv LX et al., 2021, Late Cenozoic thrust propagation within the Keping fold-and-thrust belt along the southern foreland of Chinese Tian Shan: Evidence from apatite (U-Th)/He results, Tectonophysics, 814, 228966.
18. Qian XY 2021, Apatite and zircon (U-Th)/He thermochronological evidence for Mesozoic exhumation of the Central Tibetan Mountain Range, Geological Journal, 56, 599-611.
19. Yu S et al., 2020, Further Evaluation of Penglai Zircon Megacrysts as a Reference Material for (U-Th)/He dating, Geostandard and Geoanalytical Research, 44(4), 763-783.
20. Chu Y et al., 2020, Cretaceous exhumation of the Triassic intracontinental Xuefengshan Belt: Delayed unroofing of an orogenic plateau across the South China Block? Tectonophysics, 793, 228592.
21. Wang Y et al., 2020, Intracontinental deformation within the Inidia-Eurasia oblique convergence zone: Case studies on the Nantinghe and Dayingjiang faults, The Geological Society of America, 132(3-4), 850-862.
22. Wang YB et al., 2020. Porphyry Mo and epithermal Au-Ag-Pb-Zn mineralization in the Zhilingtou polymetallic deposit, South China, Mineralium Deposita, 55(7), 1385-1406.
23. Sun X et al.,2021, New 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He dating for the Zhunuo porphyry Cu deposit, Gangdese belt, southern Tibet: implications for pulsed magmatic-hydrothermal processes and ore exhumation and preservation. Miner Deposita, 56, 917–934.
24. 郑波等, 2020,羌塘地块白垩纪剥蚀-冷却事件,地质论评,66(5),1143-1154.
25. Chen ZX et al., 2018, U-Th/He dating and chemical compositions of apatite in the dacite from the southwestern Okinawa Trough: Implications for petrogenesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 161, 1-13.
26. Lin W et al., 2013, Late Mesozoic compressional to extensional tectonics in the Yiwulvshan massif, NE China and its bearing on the evolution of the Yinshan-Yanshan orogenic belt--Part I: Structural analyses and geochronological constraints. Gondwana Research, 23, 54-77.
27. Lin W et al., 2013, Late Mesozoic compressional to extensional tectonics in the Yiwulvshan massif, NE China and its bearing on the evolution of the Yinshan-Yanshan orogenic belt--Part II: Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility and gravity modeling. Gondwana Research, 23, 78-94.
Ar-Ar:
|
常规阶段加热 |
激光单颗粒熔融 |
激光原位定年 | |
|
所内 |
8000元/样品 |
8000元/样品 |
400元/点 |
|
所外 |
10000元/样品 |
10000元/样品 |
500元/点 |
U-Th/He:
|
磷灰石锆石常规单颗粒溶液法 |
(U-Th)/He和U-Pb双定年 | |
|
所内 |
1500元/颗粒 |
400元/点 |
|
所外 |
2000元/颗粒 |
500元/点 |
合作研究价格给予一定优惠。
实验室位于北京市朝阳区北土城西路19号,健德桥东100米,邮编100029。中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所,2号楼205室。电话:010-82998560。